Everyday Science
Everyday Science: Key Facts- The temperature at which all of solid becomes a liquid is called its melting point
- The temperature at which all of a liquid becomes a gas is called its boiling point
- Only 2% of the world's water is in the form of ice
- The heavies solid is the element osmium
- The lightest gas is hydrogen. About 99.99% of the volume of hydrogen gas is empty space
- The average adult has a blood volume of about 5 liters
- Each day human body breathe in 15000 to 20000 liters of air
- The aveage human body contains about 250g of sodium chloride
- The most abundant element in the universe is hydrogen
- The most abundant element in the earth's crust is oxygen
- The second most abundant element in the earth's crust is silicon
- The deepest place on Earth is Mariana Trench
- Bond making is Exothermic Reaction, and Bond breaking is Endothermic Reaction
Mercury:
Mercury is the closeset planet to the sun, but it doesn’t have an atmosphere to trap the heat from the Sun. As a result, the temperature rises to 427°C at noon, and drops down to -173°C at night.
Venus:
Venus has the thickest atmosphere (97% Carbondioxide) in the solar system, causes a severe greenhouse effect, that is it traps heat from the Sun. The temperature on Venus is 461°C, and it remains same in day and night, because of large amount of heat trapped by the atmosphere.
So, the atmosphere of venus makes it the hottest planet in the solar system.
Life on Earth:
Conditions on Earth are perfect for life. We need a reasonable size of Carbondioxide for reasonable Green house effect, so that we could get reasonable heat from the Sun.
On the other hand, if we increase the size of Carbondioxide in atmosphere, it will result in more Green house effect, and the temperature on Earth will increase. And, the Earth will not remain supportive for life as other planets.
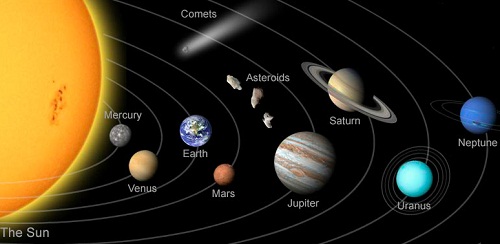
The Solar System
The Sun, Planets, Asteroids and other objects in orbits, are together known as the Solar System.
The Sun
The Sun is extremely hot and brightly glowing star of gas. It’s temperature is ranging from 6000°C on the surface to 15,000,000°C in the centre. Its energy comes from nuclear reactions deep in its core.
The Planets
The Earth is one of the eight planets in orbit around the Sun. The Planets do not have their on light, but they are visible as they reflect light from the Sun. The Planets are kept in orbit by the gravitational pull of the Sun. In general, the further a Planet is from the Sun, the slower it travels and lower its average surface temperature.
The Inner Planets
Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars are inner Planets. They are also called “rocky dwarfs”.
Mercury
Mercury is the closeset planet to the sun. It has cratered surface but it doesn’t have an atmosphere to trap the heat from the Sun. As a result, the temperature rises to 427°C at noon, and drops down to -173°C at night.
Venus
Venus is the brightest Planet. Venus has the thickest atmosphere (97% Carbondioxide) in the solar system, causes a severe greenhouse effect. The temperature on Venus is 461°C, and it remains same in day and night.
Earth
Eath is the only known Planet where conditions are perfect for life. Its distance from the Sun, and atmosphere makes it perfect for life. The Earth also has a bodyguard, Jupiter, that save it from any collision with the Asteroids.
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun in the Solar System. Mars is also called “Red Planet” because of its reddish color because of iron oxide. It has a thin atmosphere, mainly Carbon Dioxide, a dusty surface and polar caps. The rotation of Mars is also tilted like Earth that produces seasons.
The Asteroids
Asteroids are smaller objects than Planets, in orbit around the Sun. Their sizes are ranging from diameter of few kilometers to 1000km. Most Asteroids have orbits between Mars and Jupiter, and thus separates inner Planets from outer ones. Some Asteroids have much more elliptical orbits that cross the path of other Planets. So, there is possibility of collision of Asteroids with other Planets.
The outer Planets
Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune are outer Planets. They are also called "Gassy Giants".
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun in the Solar System. It is largest Planet in the Solar System. It is mainly gas and has no solid surface. Its atmosphere 90% hydrogen. The great spot on Jupiter is a huge storm that is known to have existed for centuries.
Saturn
Saturn is another gassy giant, and second largest Planet in the Solar System. It is surrounded by rings. These are not a solid mass, but millions of pieces of ice and rock.
Uranus
Uranus is another gassy giant. Its axis of rotation is tilted at more than 90. It also has rings, but much fainter than Saturn’s.
Neptune
Neptune is the outermost Planet in the Solar System It is also a gassy giant. It also has a faint ring system.
Solar System: Key Facts- There are 8 Planets in orbit around the Sun
- Mercury is the closest, and Neptune is the outermost Planet in the Solar System
- The further a Planet is from the Sun, the slower it travels, and the more time it takes to complete an orbit
- The further the Planet is from the Sun, the lower its average surface temperature. Except for Venus, where 97% Carbondioxide in the atmosphere causes severe greenhouse effect, and makes Venus the hottest Planet in the Solar System
- Mercury is the smallest, and Jupiter is the largest Planet in the Solar System
- The axis of rotation of Earth is tilted by 23.5°, and the axis of rotation of Uranus is tilted at more than 90°
SOME PROPERTIES OF PLANETS | Mercury | Venus | Earth | Mars | Jupiter | Saturn | Uranus | Neptune |
| Average distance from Sun (million km) | 58 | 108 | 150 | 228 | 778 | 1420 | 2870 | 4490 |
| Period of revolution (years) | 0.24 | 0.62 | 1.00 | 1.88 | 11.86 | 29.46 | 84.01 | 164.8 |
| Diameter at Equator (km) | 4880 | 12100 | 12800 | 6790 | 142980 | 120540 | 51120 | 49530 |
| Mass compared with Earth (Earth = 1) | 0.06 | 0.82 | 1.00 | 0.11 | 318 | 95.2 | 14.5 | 17.2 |
| Average Surface Temperature | 350°C | 480°C | 22°C | -23°C | -150°C | -180°C | -210°C | -220°C |
| Average Density (g/cm^3) | 5.4 | 5.2 | 5.5 | 3.9 | 1.3 | 0.7 | 1.3 | 1.8 |
| Surface gravity at equator (m/s^2) | 3.78 | 8.60 | 9.78 | 3.72 | 22.9 | 9.05 | 7.77 | 11.0 |
| Number of Moons | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 52 | 30 | 21 | 8 |
 How important the Atmosphere is....??
How important the Atmosphere is....??
Mercury is the closest planet to the Sun, then why Venus is more hotter than Mercury?
Size of Jupiter in comparison with Earth

Size of Sun in comparison with Gassy Giants (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune)
SOME COMMON ALLOYS| Alloy | Mixture of Metals |
| Steel | Iron, Carbon |
| Cupronickel | Copper, Nickel |
| Bronze | Copper, Tin |
| Brass | Copper, Zinc |
| Solder | Lead, Tin |
| Pewter | Tin, Lead |
| Constantan | Copper, Nickel |
| Magnalium | Aluminium, Magnesium |
| Duralumin | Aluminium, Copper, Magnesium |
| Amalgams | Mercury, Tin (Used for fillings in teeth) |
| German Silver | Copper, Nickel, Zinc |
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN SCIENTIFIC TERMS| Scalars | Vectors |
Quantities which have magnitude only, and no direction are called Scalars.
For example, Speed, Temperature, Mass etc. | Quantities which have a direction as well as a magnitude are called Vectors.
For example, Velocity, Weight, Force etc. |
| Speed | Velocity |
| Rate of change of distance is called Speed. For example, This car can travel with speed 80m/s. Speed can be calculated as: Speed = Distance / Time | Velocity means the speed of something and its direction of travel.
For example, A car is moving with velocity 80m/s towards East. |
| Heat | Temperature |
Heat is the energy an object has because of the movement of its atoms and molecules. Heat depends on the size or type of object.
For example, A 1000 watt light bulb will give off more heat as compare to 100 watt light bulb. | Temperature is not energy, but a measure of it. Temperature does not depend on the size or type of object.
For example, the temperature of a small cup of boiling water is the same as the temperature of a large pot of boiling water. |
| Periscope / Telemeter | Perimeter |
Periscope:
A Periscope is a scientific instrument for observation from a concealed position.
Telemeter:
A Telemeter is a scientific instrument for measuring distance from observer. | A perimeter is the length of boundaries or outer lines of an object. For example,  The perimeter of this rectangle is:
Perimeter = 4 + 4 + 2 + 2 = 12 inches |
| Microscope | Telescope |
| Microscope is a scientific instrument for magnifying small objects. | Telescope is a scientific instrument for viewing objects at great distances. |
| Element | Molecule |
| An Element is a single substance which cannot be split into two or more simpler substances by chemical means. | A Molecule is the smallest particle of a compond. Molecules are made up of two or more atoms. |
| Mixture | Compound |
When two or more atoms or molecules combine together, they form Mixture.
For example, Alloys are mixture of two or more metals, so they contain two or more different types of atoms.
Other Differences:
1. It can be separated by physical means.
2. Its physical properties are intermediate between those of the substances in it.
3. A mixture's composition can vary.
4. Its chemical properties are the result of the substances in the mixture. | When two or more elements chemically combine together, they form Compounds. Compounds are pure substances as they contain only one type of molecules, e.g. Water, Carbon dioxide.
Other Differences:
1. It cannot be separated by physical means.
2. Its physical properties are individual and not the result of its elements.
3. A compound's composition cannot vary.
4. Its chemical properties are quite different from those of its elements. |
| Atomic Number | Mass Number |
| The atomic number of an element is the number of protons or electrons in its atom. | The mass number of an element is the total number of protons and neutron in its atom. |
| Isotopes | Isomers |
Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. As they contain same number of protons or electrons, so chemically they are identical. But, as they have different number of neutrons, so they have different masses.
For example, Deuterium is isotopes of Hydrogen. Both have same atomic number (1). But different mass number: Hydrogen = 1; Deuterium = 2 | Molecules with identical molecular formulae but with different structural formulae are called Isomers.
For example,
Butane and Isobutane are isomers because they have same molecular formulae, but different structure.
As they have different structures, so they have different physical properties. And, as they have identical molecular formulae, so they react in a similar way. |
| Reversible Reaction | Irreversible Reaction |
| A chemical reaction that can proceed in both directions; from reactants to products, and from products to reactants, is called Reversible Reaction. | A chemical reaction that can proceed in one direction only; from reactants to products, and NOT from products to reactants, is called Irreversible Reaction. |
| Endothermic Reaction | Exothermic Reaction |
| A chemical reaction which takes in energy (heat) and involves bond breaking is called Endothermic Reaction. | A chemical reaction which gives out energy (heat) and involves bond making is called Exothermic Reaction. |
| Oxidation | Reduction |
Oxidation is a/an:- gain of oxygen
- loss of hydrogen
- loss of electron
- increase in oxidation state
| Reduction is a:- loss of oxygen
- gain of hydrogen
- gain of electron
- decease in oxidation state
|
| Anode | Cathode |
| The anode is the electrode connected to the positive terminal of a cell (battery). | The cathode is the electrode connected to the negative terminal of a cell (battery). |
Alloys
Mixture of two or more Metals is called Alloy. By mixing Metals, we usually improve the quality of Metals.
For example, Steel an alloy of Iron is stronger than Iron is made by adding 99% Iron with 1% Carbon.
Metals: Key Facts- Over 75% of the elements in the Periodic Table are Metals
- The metal having lightest density is Lithium
- The metal having heavyiest density is Osmium
- The metal having lowest melting point is Mercury
- The metal having highest melting point is Tungsten
- The most expensive metal is Platium
- The most rarest metal is Rhodium
- The most abundant metal is Aluminium
- The most inert (unreactive) metal is Iridium
- The most reactive metal is Francium
- The most brittle metal is Manganese
AirAir is a mixture of gases. Its composition is:
| Component | Composition by Volume |
| Nitrogen | 78% |
| Oxygen | 21% |
| Noble gases | 1% (mainly argon) |
| Carbon Dioxide | 0.03% |
NitrogenNitrogen gas is essential for the formation of all animal and plant proteins.
OxygenAll animal and plants need Oxygen for respiration. Oxygen is essential for combustion.
Carbon DioxideCarbon dioxide is used in fire extinguisher. It is used to deep-freeze and preserve food. It is used in carbonated drinks.
Computer NetworkA computer network is a group of connected communicating devices such as Computers and Printers.
Local Area Network (LAN)A local Area Network (LAN) is a computer network that connects computers and other devices in a limited geographical area such as college, university, office building etc.
internet (lower case letter)An internet is two or more networks that can communicate with each other.
InternetThe Internet is collaboration of more than hundreds of thousands interconnected networks. The Internet allows communication and data sharing among hundreds of thousands interconnected networks.